eHealth & Emergency domain
eHealth is certainly one of the most promising fields in which new technologies will play a fundamental role. Impacts are expected to be essentially in three main areas reported hereafter:
- Data transmission: increasingly performing technologies in terms of bitrate, latency, security, and resilience enable previously unfeasible use cases.
- Peripheral devices: These are innovative viewers for augmented reality/virtual reality (AR/VR) or ever more innovative prostheses.
- Software solutions: mainly based on innovative techniques of machine learning (ML) and AI.
In the following sections it is reported how SNS and future network technologies can benefit eHE domain and that will be deployed as part of the trials performed by TrialsNet.
eHealth
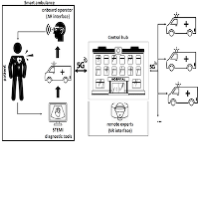
Telemedicine: SNS and 5G/B5G systems consisting in high-speed, low-latency connections allow for medical images and other data to be transmitted quickly and accurately. So, it is possible to transmit data about a patient’s health to healthcare professionals in real time, even in mobility situations, permitting pre-hospital identification of the correct diagnosis and management strategy in chest pain patients may lead to a better disease outcome.
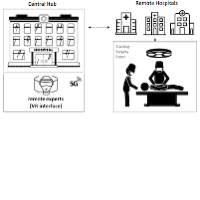
Remote Monitoring: SNS and 5G/B5G systems, together with AR/VR and telepresence technologies can represent a revolution in remote monitoring and proctoring in the interventional cardiology sector. In this way it may be possible, even in areas not equipped with departments for certain medical specializations, to be assisted by the specialised medical doctors’, especially in the surgical field.
Control of Prothesis: A smart prosthesis is an application product that combines cognitive imaging and control technology, enabled by radio connectivity to allow a prosthetic device control system with AI technologies for reducing the need for explicit control by the user and thus their cognitive load for driving it. This type of prosthesis control makes the movements of the wearer more natural.
Emergency
SNS and 5G/B5G systems open a new possibility to mass causality incidents. In fact, currently, emergency services in case of accidents are based on predefined Emergency Action Plans, lacking the flexibility to address different dynamic plans and guidelines. Moreover, even though a massive number of sensors and connected devices such as smartphones, tablets, wearables, etc., are available on market, they are not currently used in emergencies. Where demand for medical assistance and resources is greater than that available, the priority must be to identify those who are most in need of medical attention. Strengthening health system preparedness for MCI has become a priority for the European Strategy, therefore preparedness, management, and minimisation of the consequences of MCI will be investigated in this use case. Similar concepts apply when rescuing a patient in a densely crowded area, where it is paramount to achieve very fast reaction times which can improve substantially the survival rate in these contexts.